38 Degrees F To C
cibeltiagestion
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
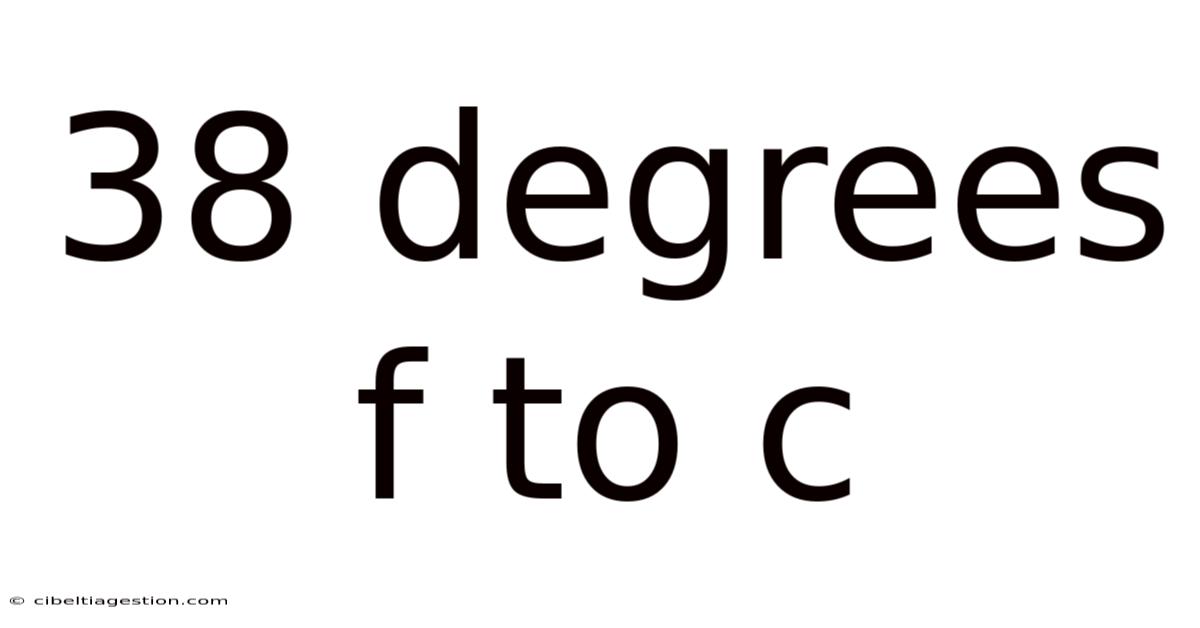
Table of Contents
Converting 38 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you wondering how to convert 38 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C)? This seemingly simple conversion is a fundamental concept in understanding temperature scales and is frequently encountered in everyday life, from checking the weather forecast to adjusting oven temperatures. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 38°F to °C but also explain the underlying principles, provide alternative methods, and delve into the historical context of these temperature scales. We'll even address some common FAQs to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before diving into the conversion, it's crucial to understand the difference between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales. Both are used to measure temperature, but they have different reference points.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, defines the freezing point of water as 32°F and the boiling point as 212°F, at standard atmospheric pressure. The scale is based on a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride as its zero point.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius was developed by Anders Celsius in the 18th century. It defines the freezing point of water as 0°C and the boiling point as 100°C, at standard atmospheric pressure. This scale is more widely used globally than Fahrenheit.
The difference in reference points is why a direct conversion is necessary. You can't simply add or subtract a constant value to convert between the two scales.
Converting 38°F to °C: The Formula
The most common and accurate method for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius involves a simple formula:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 38°F:
°C = (38 - 32) × 5/9
°C = 6 × 5/9
°C = 30/9
°C ≈ 3.33
Therefore, 38 degrees Fahrenheit is approximately equal to 3.33 degrees Celsius.
Alternative Methods and Tools
While the formula is the most precise method, there are alternative ways to perform this conversion:
-
Online Converters: Numerous websites and applications offer online temperature converters. Simply input the Fahrenheit value, and the converter will instantly provide the Celsius equivalent. These tools are convenient for quick conversions, but understanding the underlying formula remains valuable.
-
Temperature Conversion Charts: Printed or digital temperature conversion charts provide a visual representation of Fahrenheit and Celsius equivalents. These charts are useful for quick reference, especially if you frequently need to convert between the two scales. However, they usually don't offer the same level of precision as the formula.
-
Approximation Methods: For quick estimations, you can use a simplified approximation. Subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature and then dividing by 2 provides a reasonably close approximation, although it's less accurate than the formula. This method is suitable when high precision is not required.
The Scientific Significance of Temperature Conversion
Accurate temperature conversion is crucial in various scientific fields. Inaccurate conversions can lead to significant errors in experimental results and data analysis. Some key areas where precise temperature conversion is critical include:
-
Chemistry: Chemical reactions are highly temperature-dependent. Precise temperature control and accurate conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius are essential for replicating experiments and ensuring accurate results.
-
Physics: Many physical phenomena, such as the behavior of gases and the expansion of materials, are directly affected by temperature. Accurate conversion is vital for interpreting experimental data and developing theoretical models.
-
Meteorology: Weather forecasting relies heavily on temperature measurements. Converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius is necessary for consistent global weather reporting and analysis.
-
Engineering: In engineering applications, from designing HVAC systems to creating specialized materials, precise temperature control and conversion are crucial for performance, safety, and efficiency. Incorrect conversions can have serious consequences.
-
Medicine: In medical applications, precise temperature monitoring is vital for patient care and diagnosis. Converting between temperature scales is essential for accurate record-keeping and communication between medical professionals using different systems.
A Deeper Dive into the History of Temperature Scales
Understanding the history of the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales provides context for their differences.
-
Fahrenheit Scale: While Fahrenheit's precise methodology is debated, it is believed he initially defined his zero point using a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride. He subsequently redefined his scale based on the freezing and boiling points of water, which led to the scale we use today. His scale was initially widely adopted, particularly in Europe and North America.
-
Celsius Scale: Originally called the centigrade scale (meaning "divided into 100 degrees"), the Celsius scale was developed by Anders Celsius. He initially defined 0°C as the boiling point of water and 100°C as the freezing point, later reversed by his colleagues for practical reasons. The Celsius scale gained prominence globally, especially within the scientific community, and eventually became the preferred standard in most parts of the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A1: Historically, different scales arose independently due to varying scientific approaches and regional preferences. The Fahrenheit scale gained early traction, particularly in the English-speaking world, while the Celsius scale gained broader acceptance due to its logical structure and global standardization.
Q2: Is there a formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A2: Yes, the reverse formula is: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Q3: Which scale is more accurate?
A3: Both scales are equally accurate in measuring temperature. The difference lies solely in their reference points and the numerical values assigned to those points.
Q4: What is the absolute zero point in Celsius?
A4: Absolute zero, the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases, is -273.15°C.
Q5: Are there other temperature scales besides Fahrenheit and Celsius?
A5: Yes, several other scales exist, including Kelvin (used extensively in science), Rankine, and Réaumur.
Conclusion
Converting 38°F to °C, while seemingly straightforward, highlights the importance of understanding different temperature scales and their underlying principles. This guide has provided not only the method for conversion but also broader context, historical background, and practical applications. Remember, while online tools offer convenience, understanding the formula remains crucial for accurate conversions and a deeper appreciation of temperature measurement. Mastering this conversion is a significant step toward a stronger grasp of fundamental scientific concepts and their relevance in everyday life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5000 Shekels Of Bronze Weight
Sep 13, 2025
-
How Much Is 350 Ml
Sep 13, 2025
-
Algebra Equations That Equal 16
Sep 13, 2025
-
Level H Answers Reading Plus
Sep 13, 2025
-
4 11 Ft To Inches
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 38 Degrees F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.